CX-0044 ECLASS v1.0.2
ABSTRACT
ECLASS1 is an international cross-industry master-data business standard for products and services information to be exchanged. The ECLASS data dictionary is based on ISO and IEC standards and is an important enabler for interoperability. ECLASS is since 2000 in the market and widespread used in many industries. Therefore, ECLASS has a state-of-the-art infrastructure and experience to further develop and maintain a semantic dictionary.
The Asset Administration Shell (AAS) has standardized the structure including the different submodels defined in IDTA, and ECLASS has standardized the semantics for information elements used for the definition of digital twins.
ECLASS is the recommended dictionary by Plattform Industrie 4.0 for the creation of Asset Administration Shell and Digital Twins. Therefore, ECLASS is to be preferred within Catena-X for the semantic description of models and their attributes. Thus, if the semantic description of an asset or its properties is available in the ECLASS dictionary, then it shall be used. If it is not part of ECLASS, alternatives can be used. In parallel, a change request should be made to ECLASS to add the necessary information in the next release so that it is available for Catena-X in the future.
1. Introduction
1.1 Audience & Scope
This section is non-normative
The standard is relevant for:
- Data Provider / Consumer
- Enablement Service Provider
- Consulting Services Provider
The standard is relevant for the description of assets and their properties.
1.2 Context
ECLASS2 is a cross-industry master-data business standard for products and services information to be exchanged in a computer-sensible form across all borders -- across sectors, countries, languages, and organizations. The ECLASS data dictionary is based on ISO 13584-42 and IEC 61360-2. It is used, for instance, for the exchange of product data for procurement, eCommerce, and engineering tools.
ECLASS is a formal semantic dictionary that is used for product description and product classification. The information model used by ECLASS is the foundation for the classification and description of products and services. It allows the reuse of generic descriptions in multiple business domains, the mapping to other dictionaries, and ensures the upgradability of the ECLASS dictionary.
ECLASS is recommended by Plattform Industrie 4.0 for the creation of Asset Administration Shell and Digital Twins3.
The Asset Administration Shell (AAS) has standardized the structure (including the different submodels defined in IDTA), and ECLASS has standardized the semantics for information elements used for the definition of digital twins.
ECLASS is seen as a key element of an AAS and integral for semantic interoperability in its submodels. The document4 "Modelling the Semantics of Data of an Asset Administration Shell with Elements of ECLASS" provides modeling details.
1.3 ECLASS Overview
The data model of ECLASS is shortly depicted in ECLASS website5. ECLASS is a formal semantic dictionary which is used for product description and product classification. The ECLASS dictionary is maintained in Releases. Each Release is containing an exhaustively defined and reproduceable set of structure elements.
ECLASS uses globally unique identifiers for every Structure Element included in the ECLASS Standard. This globally unique identifier is called IRDI (International Registration Data Identifier). These identifiers are used to ensure that the semantic of an element is unique in the overall system. The IRDI is based on the international standards ISO/IEC 11179-6, ISO 29002, and ISO 6532. Every institution registered by the registration authority has a unique ICD (International Code Designator) identifier. In the case of ECLASS this is the "0173". ECLASS Dictionary provides IRDIs for all Structure Elements e.g., Classification Classes, Application Classes, Properties, Units of Measure, Property Values (in case of coded values), Value Lists, Aspects, Blocks and Templates. For example, the IRDI 0173-1#02-AAO677#002 stands for a property defining the "Manufacturer name".
ECLASS is an open standard based on global IEC standards. The development is openly designed, content can be contributed by anyone, the data model is open and licensed free of charge for the recipients of the data. An ECLASS license is needed to describe commercial products. Additional details can be obtained from the ECLASS website6. For testing and development of Catena-X models there is no cost. In addition, ECLASS recently released Release 13 with the Asset XML containing IDTA submodels, which are also free of charge also for productive use.
Details on the model can be acquired from the ECLASS conceptual data model specs7.
1.4 Conformance
As well as sections marked as non-normative, all authoring guidelines, diagrams, examples, and notes in this specification are non-normative. Everything else in this specification is normative.
The key words MAY, MUST, MUST NOT, OPTIONAL, RECOMMENDED, REQUIRED, SHOULD and SHOULD NOT in this document are to be interpreted as described in BCP 14 [RFC2119] [RFC8174] when, and only when, they appear in all capitals, as shown here.
1.5 Proof of Conformity
This section is non-normative
ECLASS is relevant to all semantic models developed in Catena-X which in future releases should utilize ECLASS for semantic interoperability. Future releases may include all model reference implementations and relative processes.
All participants and their solutions will need to prove that they conform to the Catena-X standards. To validate that the standards are applied correctly, Catena-X employs Conformity Assessment Bodies (CABs).
The concept description of an AAS Element can be defined with elements of ECLASS. In general, the principle followed is to make semantics explicitly by using standardized ECLASS Elements.
To prove conformity, the resulting semantic models developed SHOULD
-
utilize ECLASS for the semantic description of assets by using the respective IRDIs.
-
explicitly state the absence of the specific attributes in ECLASS as justification of not using it.
1.6 Examples
ECLASS has released a document^2^ describing how AAS and ECLASS can be utilized. More specific documents for the use of ECLASS within the AAS are on the way. All of it will be available on the ECLASS and IDTA website.
The essential functional elements of the AAS are submodels, which comprise descriptive properties, configuration parameters, variables, files, offered capabilities and operations of the asset in a machine-interpretable form. Submodels are information models that describe a specific aspect of an asset. Each submodel and all its elements have a semantic ID. This semantic ID is inherited by submodels, submodel elements, qualifiers and views and is a reference to a unique identifier. Extensions and external asset IDs also exist. These elements do also have a semantic ID.
The ECLASS standard should be used for this semantic ID. The concept description of an AAS Element can be defined with elements of ECLASS. In general, the principle followed is to make semantics explicitly by using standardized ECLASS Elements.
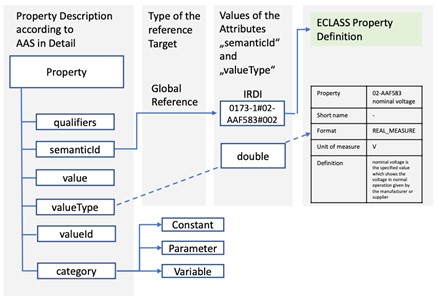
Figure: Mapping of a Property with different Categories to an ECLASS Property3
ECLASS, with its Release 13.0 in 2022, contains enhancements for the Asset Administration Shell (AAS). Regarding the data model, a new application class of type "Asset" has been introduced in addition to BASIC and ADVANCED. Furthermore, features can have the data types "File" and "Blob". In addition, AAS submodel templates were adhering to the IDTA standardized submodels "Handover Documentation" and "Digital Nameplate for Industrial Equipment".
Further technical details can be found in the respective webpage8.
1.7 TERMINOLOGY
This section is non-normative
AAS Asset Administration Shell
IRDI
International Registration Data Identifier
IDTA
Industrial Digital Twin Association e.V.
Additional terminology used in this standard can be looked up in the glossary on the association homepage.
2. Usage of ECLASS Semantics in Catena-X
This section is normative
The usage of ECLASS in Catena-X standardized semantic models is an important enabler for interoperability. If any model is to be standardized in Catena-X according to "CX-0003 Semantic Aspect meta model (SAMM)", then it SHOULD be checked if ECLASS can cover parts of the model with appropriate semantic descriptions.
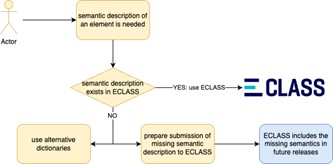
Figure: Process of semantic description with ECLASS
Specifically, as shown in Figure 1, the following investigative steps SHOULD be carried out:
- If the semantic description of an asset or its properties exists in the ECLASS dictionary, then it SHOULD be used to describe it.
- In case the ECLASS dictionary does not have the necessary information then:
- Alternatives MAY be used, e.g., own, or alternative dictionary.
- In parallel a request SHOULD be made to ECLASS to add the necessary information in its next release so that this can be used in the future.
ECLASS is an open standard which is constantly further being developed to respond to changes in the market. As such, anyone independent whether they are ECLASS members or not, can submit change requests in order to introduce or revise ECLASS content. Hence, as shown in Figure 1, such a submission SHOULD be made to ECLASS. Subsequently, when ECLASS introduces the needed changes in its future release, the Catena-X model SHOULD use the requested content. Further info on how such requests can be submitted to ECLASS is described in detail on the respective ECLASS webpage9.
3. References
3.1 Normative References
The ECLASS10 website provides concrete info and tools with respect to understanding and utilizing the ECLASS standard.
3.2 Non-Normative References
This section is non-normative
In addition to the ECLASS11 website additional documents enable the better understanding of ECLASS usage in conjunction with Asset Administration Shell and Digital Twins^2^. The ECLASS Release 13.0 contains enhancements for the Asset Administration Shell (AAS) that include a new application class of type "Asset". Technical details can be found on the respective webpage12.
Legal
Copyright © 2025 Catena-X Automotive Network e.V. All rights reserved. For more information, please visit here.