CX-0092 Aspect Model: Quality Task Attachment v1.0.1
ABSTRACT
During collaborative work on a Quality Task, it may be necessary to share additional data and files which cannot be standardized and are not available in existing semantic models with the Quality Task collaborators. To make this possible, the semantic model "Quality Task Attachment" describes the type and structure of the data and files and links them to an existing QualityTask.
1. INTRODUCTION
This document describes the semantic model "Quality Task Attachment" used in the Catena-X network.
1.1 AUDIENCE & SCOPE
This section is non-normative
This standard is relevant for the following roles:
- Data Provider / Consumer
- Business Application Provider
1.2 CONTEXT
This section is non-normative
The Catena-X use case Live Quality Loops (QAX) uses multiple data models to exchange data between automotive manufacturer (OEM) and component supplier (TIER1). Each of these data models can be supplied independently.
The QualityTaskAttachment data model describes a way to exchange data and files, which are not available in the existing data models, in the context of a QualityTask. In order to make the non-standardized data and files machine understandable, they are described using the "Quality Task Attachment" model.
1.3 CONFORMANCE
As well as sections marked as non-normative, all authoring guidelines, diagrams, examples, and notes in this specification are non-normative. Everything else in this specification is normative.
The key words MAY, MUST, MUST NOT, OPTIONAL, RECOMMENDED, REQUIRED, SHOULD and SHOULD NOT in this document document are to be interpreted as described in BCP 14 [RFC2119] [RFC8174] when, and only when, they appear in all capitals, as shown here.
1.4 PROOF OF CONFORMITY
This section is normative
All participants and their solutions will need to prove they conform with the Catena-X standards. To validate that the standards are applied correctly, Catena-X employs Conformity Assessment Bodies (CABs).
For Data Provider: To prove conformity you have to fulfill all MUST criteria mentioned in chapter Normative criteria for Data Provider.
There is no proof of conformity necessary for Data Consumer.
For Business Application Provider: To prove conformity you have to fulfill all MUST criteria mentioned in chapter Normative criteria for Business Application Provider.
A model validator must be created, to prove the correctness of the data model. A generic test set created for the model must prove the expected results.
The proof of conformity for a single semantic model is done according to the general rules for proving the conformity of data provided to a semantic model or the ability to consume the corresponding data.
1.5 EXAMPLES
Example playload in JSON format:
{
"relatedModelType" : "fleet.claim_data",
"qualityTaskId" : "BPN-811_2022_000001",
"files" : [ {
"schema" : {
"delimiter" : "semicolon",
"variables" : [ {
"unit" : "degreeCelsiusPerHour",
"variableName" : "Price",
"dataType" : "double",
"variableDescription" : "This column contains the hourly temperature of a part"
} ],
"decimalSeperator" : "\"comma\", \"dot\""
},
"fileDescription" : "Price list for various components",
"fileName" : "Histogramm_data.csv",
"sizeInKb" : 615,
"fileExtension" : "csv",
"filePath" : "/subfolder/Histogramm_data.csv"
} ],
}
1.6 TERMINOLOGY
This section is non-normative
Aspect Model
An Aspect Model is a formal, machine-readable semantic description (expressed with RDF/turtle) of data accessible from an Aspect.
An Aspect Model must adhere to the Semantic Aspect Meta Model (SAMM), i.e., it utilizes elements and relations defined in the Semantic Aspect Meta Model and is compliant to the validity rules defined by the Semantic Aspect Meta Model.
Aspect model are logical data models which can be used to detail a conceptual model in order to describe the semantics of runtime data related to a concept. Further, elements of an Aspect model can/should refer to terms of a standardized Business Glossary (if existing).
Business Partner Number (BPN)
A BPN is the unique identifier of a partner within Catena-x.
Additional terminology used in this standard can be looked up in the glossary on the association homepage.
2 ASPECT MODEL QUALITY TASK ATTACHMENT
This section is normative
2.1 INTRODUCTION
Catena-X use case "Live Quality Loops"(QAX) uses several Catena-X standardized data models to exchange data:
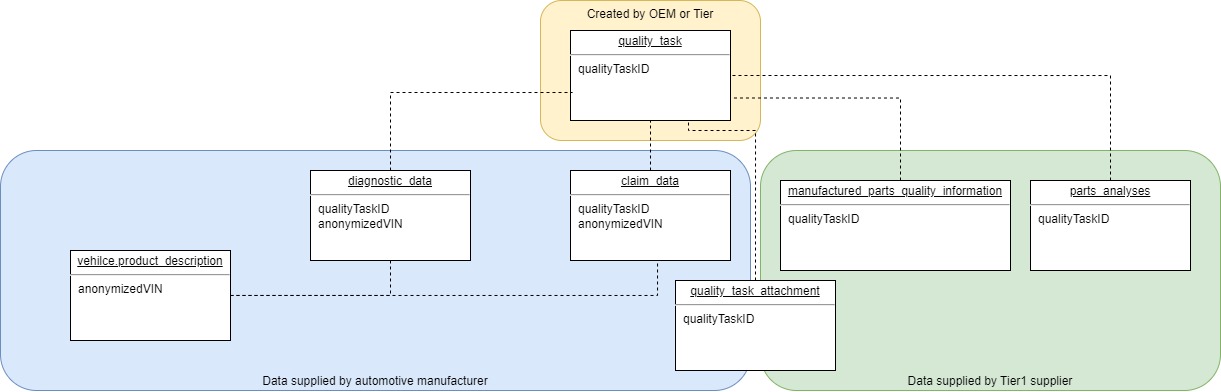
Figure 1: Hierarchy of Catena-X data models used in QAX
Data models in QAX and their content:
-
QualityTask is the root element and describes why companies are working together on a quality topic and what they want to do. All involved companies and their contact people are named. In addition, a flag tells what should be done with exchanged data after a QualityTask is closed.
-
Vehicle.ProductDescription: This data model is a representation of one vehicle affected by this QualityTask. The model represents the vehicle when it was sold to the end-customers from an end-customers point of view: Which standard equipment was installed in the vehicle and which extra equipment was installed in the vehicle.
-
Fleet.DiagnosticData: Diagnostic data coming from multiple vehicles that are affected by this QualityTask + Diagnostic data from similar vehicles that are not affected by this QualityTask.
-
Fleet.ClaimData: Customer complaints that are linked to this QualityTask + Data about the exchange of potentially faulty parts
-
ManufacturedPartsQualityInformation: A selection of manufacturing-related parameters that help to solve the QualtiyTask
-
PartsAnalyses: Analyses results of replaced and potentially faulty parts that are linked to this QualityTask
-
QualityTaskAttachment: Description of additional data and files that are linked to this QualityTask
2.2 NORMATIVE CRITERIA
The usage of the described semantic model "Quality Task Attachment" is a MUST for Data Provider and Data Consumer that want to exchange data over Catena-X automotive network, which is related to a QualityTask but not covered in other semantic models.
2.2.1 NORMATIVE CRITERIA FOR DATA PROVIDER
Every data provider MUST provide the data conformant to the semantic model specified in CX - 0092.
If available the identifier of QualityTask SHOULD be provided.
In the Catena-X data space "Quality Task Attachment" data MUST be exchanged via Eclipse Dataspace Connector (EDC) conformant to CX - 0018.
It is RECOMMENDED to store the data from "Quality Task Attachment" and the files described in it within a ZIP compressed folder. This ZIP compressed folder and EDC S3 data plane should be used to exchange "Quality Task Attachment" data.
2.2.2 NORMATIVE CRITERIA FOR BUSINESS APPLICATION PROVIDER
It is a MUST for Business Application Provider to support at least 2 standardized Catena-X QAX aspect models from Catena-X Release 3.2 (2 out of Catena-X standards CX - 0036, CX - 0037, CX - 0038, CX - 0039, CX - 0040, CX - 0041, CX - 0091, CX - 0092) to get the label "Catena-X Certified Solution" for their quality application.
It is RECOMMENDED for Business Application Provider to be able to read the semantic model "Quality Task Attachment".
2.3 SPECIFICATION ARTIFACTS
The modeling of the semantic model specified in this document was done in accordance to the "semantic driven workflow" to create a submodel template specification.
This aspect model is written in SAMM 2.0.0 as a modeling language conformant to CX-0003 as input for the semantic driven workflow.
Like all Catena-X data models, this model is available in a machine-readable format on GitHub conformant to CX-0003.
2.4 LICENSE
This Catena-X data model is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC-BY-4.0) license, which is available at Creative Commons1.
2.5 FORMATS OF SEMANTIC MODEL
2.5.1 RDF TURTLE
The rdf turtle file, adhering to the Semantic Aspect Meta Model, is the master for generating additional file formats and serializations. It is provided here:
urn:samm:io.catenax.quality_task_attachment:1.0.0
This identifier MUST be used by the data provider to define the semantics of the data being transferred.
The open source command line tool of the Eclipse Semantic Modeling Framework2 is used for generation of other file formats like for example a JSON Schema, aasx for Asset Administration Shell Submodel Template or a HTML documentation.
2.5.2 JSON SCHEMA
A JSON Schema and a JSON sample payload can be generated from the RDF Turtle file using the Eclipse ESMF tooling.
If present, example JSON-payloads MUST validate against the generated JSON schema.
3. REFERENCES
3.1 NORMATIVE REFERENCES
- CX - 0003 SEMANTIC ASPECT META MODEL
- CX - 0004 GOVERNANCE PROCESS FOR SEMANTIC MODELS
- CX - 0018 ECLPISE DATA SPACE CONNECTOR (EDC)
- CX - 0036 Aspect Model: QualityTask
- CX - 0037 Aspect Model: Vehicle.ProductionData
- CX - 0038 Aspect Model: Fleet.DiagnosticData
- CX - 0039 Aspect Model: Fleet.ClaimData
- CX - 0040 Aspect Model: PartAnalyses
- CX - 0041 Aspect Model: ManufacturedPartsQualityInformation
- CX - 0091 Aspect Model: Fleet.Vehicles
- CX - 0092 Aspect Model: QualityTaskAttachment
Legal
Copyright © 2024 Catena-X Automotive Network e.V. All rights reserved. For more information, please visit here.